Modern digital products need strong protection from the moment they are built. Users expect safe platforms, businesses depend on trust, and even small security issues can cause big problems later. As companies move faster toward full-stack JavaScript development, the MERN stack—MongoDB, Express.js, React, and Node.js—has become one of the top choices. But even with its power and speed, it still needs the right security steps to keep data safe.
In today’s world, security cannot be optional. It must be part of the planning, coding, and deployment process. This guide explains how software development teams can use simple and practical steps to secure every part of a MERN application. The goal is to help agencies, developers, and businesses understand how to protect user data, stop attacks, and build systems that stay safe as they grow.
You will also find helpful examples from one of our MERN-based platform case studies, such as this project:
Stable Hub Case Study
and insights from our technical articles on MERN stack security. These real examples show how early planning and the right security practices can create smooth and safe products.
By the end of this guide, you will have a clear understanding of how to build secure MERN apps using easy methods without adding complexity or slowing down your development process.
1. Why Security Is Important in MERN Applications
The MERN stack gives developers one language to work with across the server, database, and frontend. This brings speed and consistency. But because everything is connected, a weak spot in one layer can affect the entire system.
For example, if database access is not protected, attackers could read or change private user data. If API endpoints are left open, bots may attack your server. If the frontend is not secured, users may be exposed to harmful scripts.
This is why MERN security must be taken seriously from the first day of development. Planning ahead helps prevent risks, reduce fixes later, and keep customer trust. You can also explore detailed best practices here:
MERN Stack Security Best Practices
2. Secure Coding Practices for MERN Developers
Secure apps begin with safe coding habits. Even small changes can protect a system from attacks.
2.1 Keep Sensitive Data Safe
Never store passwords, tokens, or database details directly in your code. Always store them in environment files such as .env and secure them on your server.
2.2 Validate All Inputs
Many attacks begin with bad input sent by bots or hackers. Validate all data before saving it or using it in your app. Simple validation protects both the database and the server.
2.3 Sanitize API Requests
MongoDB queries must be cleaned properly to prevent injection attacks. Tools like express-mongo-sanitize make this easy.
2.4 Use HTTPS Only
HTTPS encrypts the connection between the user and the server. It should be used in every modern web application.
With these simple steps, your base structure becomes stronger and supports better MERN security from the beginning.
3. Protecting Node.js and Express.js
The server layer handles the main logic of your app. Most attacks target the server because it manages sessions, authentication, and data exchange.
3.1 Use Helmet Middleware
Helmet adds security headers that protect against many common attacks.
3.2 Limit Requests
By limiting the number of API calls from one source, you can stop attacks that try to overload your server.
3.3 Set CORS Rules
CORS rules define who is allowed to access your API. This prevents unwanted apps from using your backend.
3.4 Keep Error Messages Simple
Do not show technical server errors to users. These errors give attackers information they should not have.
These steps are simple but make a big difference in MERN security for server-level protection.
4. Strengthening MongoDB Security
MongoDB stores your data, so it must be well protected.
4.1 Use Database Authentication
Never run MongoDB without a username and password. Enable proper role-based access.
4.2 Limit Permissions
Do not give full control to everyone. Give only the required access for each role.
4.3 Encrypt Data
Encrypt data both while it is stored and while it is being transferred. This helps protect user information even if something goes wrong.
4.4 Keep Backups
Regular backups save your system during issues like data corruption or accidental deletions.
These steps build a safe environment and support long-term MERN security across your database.
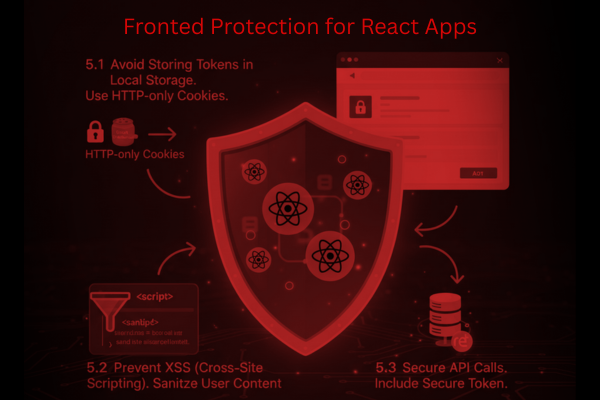
5. Frontend Protection for React Apps
React controls the user-facing experience. While React itself is secure, improper use can expose the user.
5.1 Avoid Storing Tokens in Local Storage
Tokens stored in local storage can be stolen easily. Use HTTP-only cookies instead.
5.2 Prevent XSS (Cross-Site Scripting)
Do not use unsafe HTML. Always sanitize user-generated content.
5.3 Secure API Calls
Every request to the server must include a secure token or session value.
If your app supports multiple languages or regions, extra care is needed. You can learn more here:
Internationalization & Localization in MERN
6. Designing a Secure MERN Architecture
Good security isn’t just about tools—it’s about planning the right architecture.
6.1 Clear Folder Structure
A clean structure helps avoid mistakes and makes it easier to manage code.
6.2 Automated Testing and CI/CD
Automated testing helps catch errors before they reach users. CI/CD pipelines also help push updates safely.
6.3 Regular Security Testing
Use tools like Postman tests, unit tests, and OWASP ZAP scans to identify weak areas.
6.4 Consider a Headless Architecture
Headless CMS platforms built using MERN can offer better control and safety. Learn more here:
Designing Headless CMS Platforms Using the MERN Stack
Planning a strong structure not only improves performance but also strengthens MERN security across all levels of the application.
7. Common Security Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced teams sometimes make simple mistakes such as:
- Using old and outdated packages
- Leaving MongoDB open without passwords
- Using HTTP instead of HTTPS
- Forgetting to sanitize user inputs
- Storing passwords without hashing
- Not running security tests
Avoiding these mistakes makes it much easier to maintain a safe MERN system.
MERN security
Conclusion
Security has become one of the most important parts of building any digital product. As businesses continue shifting toward the MERN stack for speed and flexibility, the need for strong protection becomes even greater. A secure app is not only safer for users—it also builds trust, prevents losses, and supports long-term growth.
A key lesson in security is that it is not something developers add at the end. It must be part of every step, from planning and coding to testing and deployment. When teams follow secure practices early, the entire development process becomes smoother, and the final product becomes stronger.
This guide has explained simple and practical steps to make MERN applications safer. These include safe server practices, strong database protection, clean React guidelines, and secure overall architecture. Each step may look small, but together they create a complete security system.
One of our recent MERN application projects, showcased here:
Stable Hub Case Study shows how early planning and strong security measures help build trustworthy apps that scale well. Our technical guides and tutorials also support development teams in applying the right security methods at every stage.
By applying these best practices consistently, you can reduce risks, protect customer data, and build systems that perform well even under pressure. Whether your product is small or large, these methods make your application stronger and safer for years ahead.
With the right mindset and regular updates, your application can achieve solid protection and deliver a safe experience for users everywhere.
FAQs
Q1: Why is MERN app security important?
It protects user data and prevents attacks.
Q2: How do I secure my API?
Use tokens, sessions, and rate limiting.
Q3: How should passwords be stored?
Always hash them before saving.
Q4: How do I protect MongoDB?
Use authentication and limit access.