What is agile project management?
Agile project management is an iterative way to deal with software advancement projects and guarantees that criticism can be followed up rapidly. Responsive changes can be made at each run or item cycle phase. This permits project groups to embrace agile management approaches to work quickly and cooperatively inside the time and spending plan.
Agile project management covers loads of various agile project management approaches, all of which draw on a few common agile standards and fundamental beliefs. In any case, there is no single widespread “agile methodology.” So, where did they generally come from? Let’s have a look at agile methodology in detail in this blog.
Definition of agile project management
It generally sounds very software development center sits back and relax. Agile project management philosophies were created considering software. Yet, the center agile qualities and agile project management standards are valuable to various groups, from item groups to promoting groups.
Knowing the history of agile project management (or possibly the rundown of it laid out above) can assist with giving a portion of the phrasing processes that describe agile project management, which we’ll take in more detail in a matter of seconds when we separate the Agile Manifesto in more detail.
However, if you’re searching for a meaning of agile project management now, rather than the history of what it used to be, here’s a proper agile project management definition.
Sound great? We should return to the Agile Manifesto to study the basic beliefs and standards you can use to direct any agile project.
Core values of agile
The agile project management focuses on software, and software engineers made the Agile Manifesto. So you’ll see that word and other related terms like “engineers” and “clients” all through.
Regardless of whether you’re making software or something entirely unexpected (like a promoting effort), there are heaps of focus points you can apply, the regardless industry you’re working in.
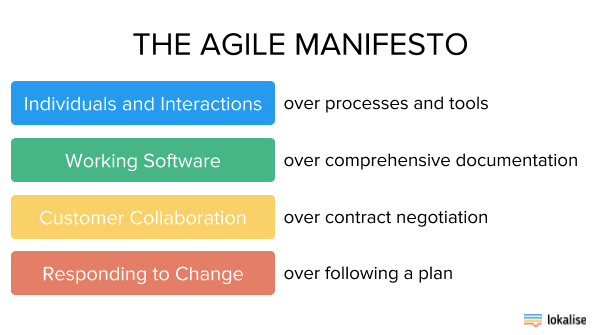
The first Agile Manifesto proclaims that agile has 4 guiding principles:
- People and cooperation over cycles and devices.
- Working software over far-reaching documentation.
- Client joint effort over agreement exchange.
- Answering to change over sticking to the script.
These fundamental beliefs are at the core of all agile project management, illuminating everything from standard ways regarding working to the 12 agile project management standards.
That applies not exclusively to the functioning cycles (progress is made through “people and communications” and “client cooperation,” putting the human component upfront), yet in addition to the completed items. The objective is to make something useful that conveys the most worth to the end client.
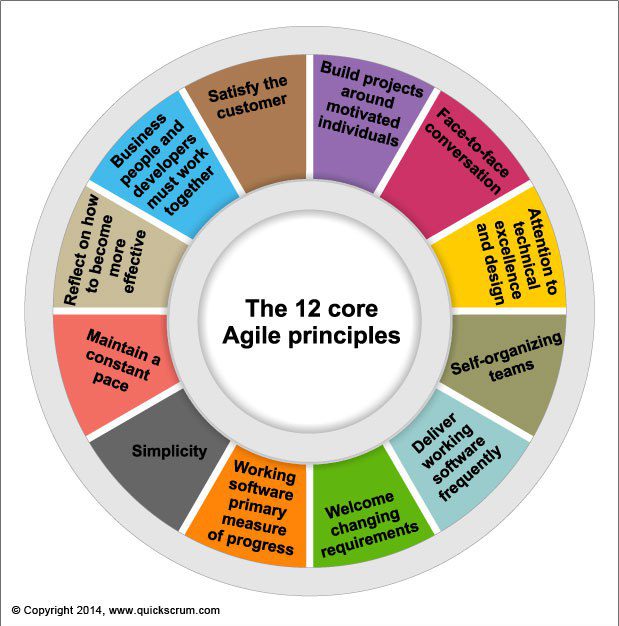
The 12 agile project management principles
The 12 principles of agile project management:
- top priority is consumer loyalty through the early and persistent conveyance of powerful software.
- Welcome evolving improvements, even late being developed. Agile cycles change for the client’s upper hand.
- Deliver working software regularly, from a long time to several months, with an inclination to the more limited timescale.
- Business individuals and engineers should cooperate every day throughout the project.
- Build projects around people. Please give them the environment and backing they need, and trust them to take care of business.
- The most proficient and powerful technique for passing data on to and inside an improvement group is up close and personal discussion.
- Working software is the essential proportion of progress.
- Agile cycles advance feasible turn of events. The backers, engineers, and clients ought to have the option to keep a consistent speed endlessly.
- Continuous regard for specialized greatness and great plan improves deftness.
- Simplicity – the art of expanding how much work is not done.
- The best structures, necessities, and plans rise out of self-putting together groups.
- At customary stretches, the group ponders how to turn out to be more compelling, then, at that point, tunes and changes its conduct appropriately.
Regardless of whether you’re discussing genuine software or involving it as a representation for anything that you’re making (we should refer to it as “The Thing”), agile strategies urge you to convey emphases of “The Thing” rapidly and regularly – because it’s better for “The Thing” to exist in defective reality than in fantastic hypothesis.
One more repeating topic in these standards? Get adjusted, remain adjusted, and cooperate. That goes for all interested parties: your group, the “money managers,” different offices, and partners. Agile project management techniques depend on a profoundly cooperative interaction and solid relational establishments. So as Bill and additionally Ted once said: be significant to one another.
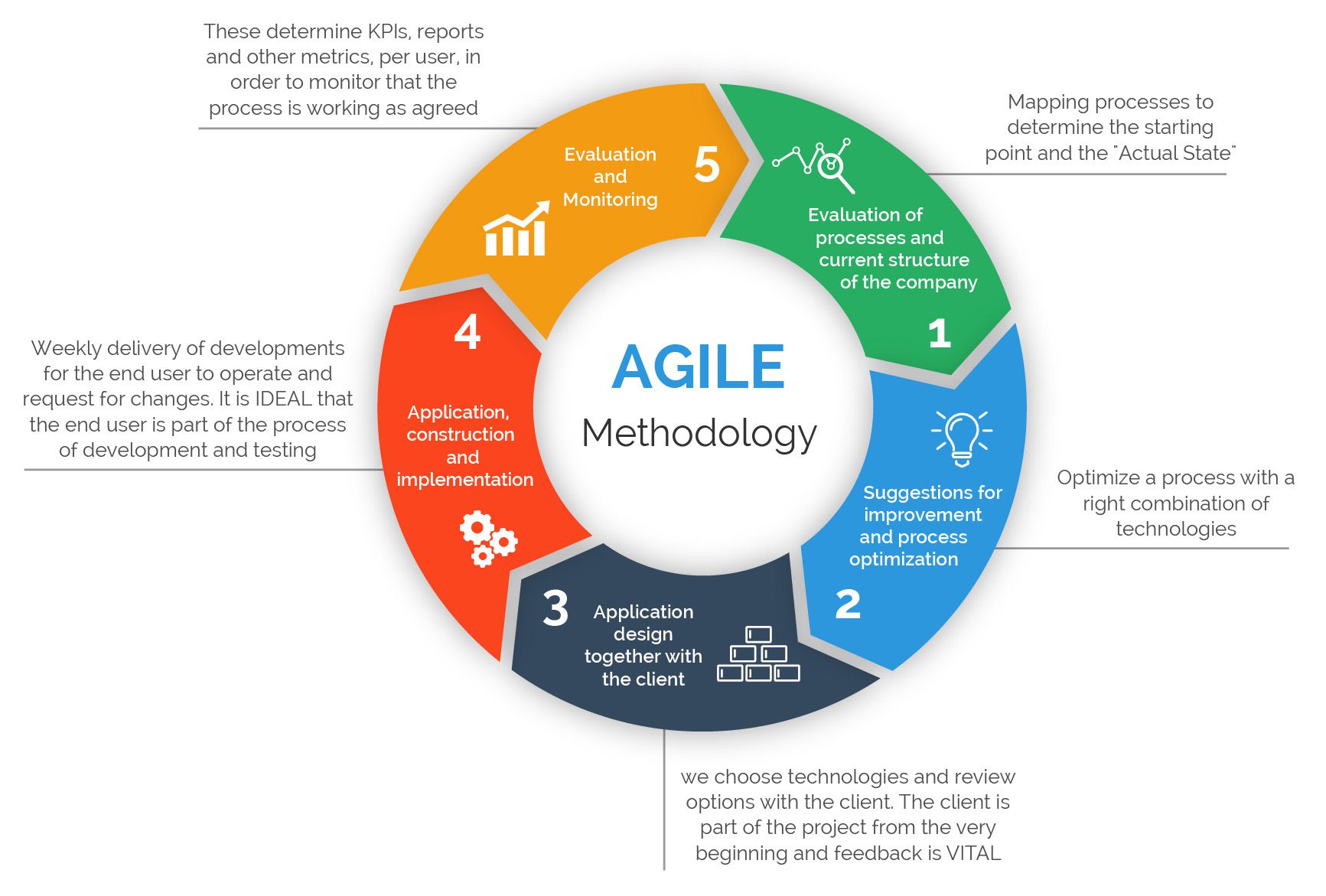
The 6 steps in the Agile methodology
The objective of Agile is to deliver more limited advancement cycles and more continuous product discharges than conventional cascade project management. This more limited time empowers project groups to respond to changes in the client’s requirements all the more actually.
You can utilize at least one or two Agile systems, as we said previously. Scrum and Kanban are two of the most well-known. In any case, each Agile approach will follow a similar essential interaction, which incorporates:
- Project planning
Like with any project, before starting, your group ought to get the ultimate objective, the worth to the association or client, and how it will be accomplished.
You can foster a project scope here, yet recall that the motivation behind utilizing Agile project management is to have the option to address changes and increases to the project effectively, so the project scope shouldn’t be viewed as unchangeable.
- Product creation
A guide is a breakdown of the highlights that will make up the eventual outcome. This is a pivotal part of the planning phase of Agile because your group will assemble these only highlights during each run.
Now, you will likewise foster a product overabundance, which is a rundown of the relative multitude of elements and expectations that will make up the eventual outcome. Your group will pull undertakings from this build-up whenever your plan runs later in.
- Release planning
In conventional cascade project management, one execution date comes after a whole project has been created. While utilizing Agile, notwithstanding, your project uses more limited improvement cycles (called runs) with highlights delivered toward the finish of each process.
Before starting the project, you’ll make an undeniable level arrangement for highlight discharges. Toward the start of each run, you’ll return to and reconsider the delivery plan for that element.
- Sprint planning
Before each run starts, the partners need to hold a run planning meeting to figure out what will be achieved by every individual during that run, how it will be accomplished, and evaluate the errand load. It’s essential to share the heap equally among colleagues to achieve their allocated assignments during the run.
Likewise, you’ll have to outwardly archive your work process for group straightforwardness, mutual perspective inside the group, and recognizing and eliminating bottlenecks.
- Daily stand-ups
To assist your group with achieving their errands during each run and survey whether any progressions should be made, hold short daily stand-up gatherings. During these gatherings, each colleague will momentarily discuss what they achieved the other day and what they will be dealing with that day.
These daily gatherings should be just 15 minutes in length. They aren’t intended to be expanded critical thinking meetings or an opportunity to discuss general news things. A few groups will even hold these gatherings were rising to keep it brief.
- Sprint survey and review
After finishing each run, your group will hold two gatherings: first, you will have a run survey with the project partners to show them the completed product. This is a significant piece of keeping open correspondence with partners. A face-to-face or video gathering meeting permits the two gatherings to construct a relationship and examine the product that emerges.
Second, you will have a run review meeting with your partners to examine what worked out positively during the run, what might have been something more, regardless of whether the errand load was excessively weighty or excessively light for every part, and what was achieved during the run.
Assuming your group is new to Agile project management, don’t skirt this fundamental gathering. It assists you with checking how much your group can handle during each run and the most proficient run length for future projects.
Benefits of Agile Project Management
Agile Project Management delivers numerous benefits below mentioned are a few of them:
- freedom – project management allows designers to chip away at models that use their assets.
- efficient utilization of assets, which empowers fast arrangement.
- more prominent adaptability and flexibility to changing necessities – designers can adjust to and roll out required improvements more readily.
- fast discovery of issues, which empowers faster fixes.
- expanded cooperation with clients, prompting products that better address client issues; and
- doesn’t need as obviously characterized objectives and cycles toward the beginning of improvement when contrasted with standard project management techniques.
Drawbacks of Agile Project Management
A few drawbacks are following:
- A project can go off course since there are fewer predetermined plans toward the beginning of a project.
- Off course projects lead to less unsurprising results.
- Agile management depends on settling on choices rapidly, so it isn’t appropriate for organizations that spend most of the day investigating issues.
- Coordinated effort between groups or end clients should consistently make an ideal product. Challenges in correspondence could affect the finished result.
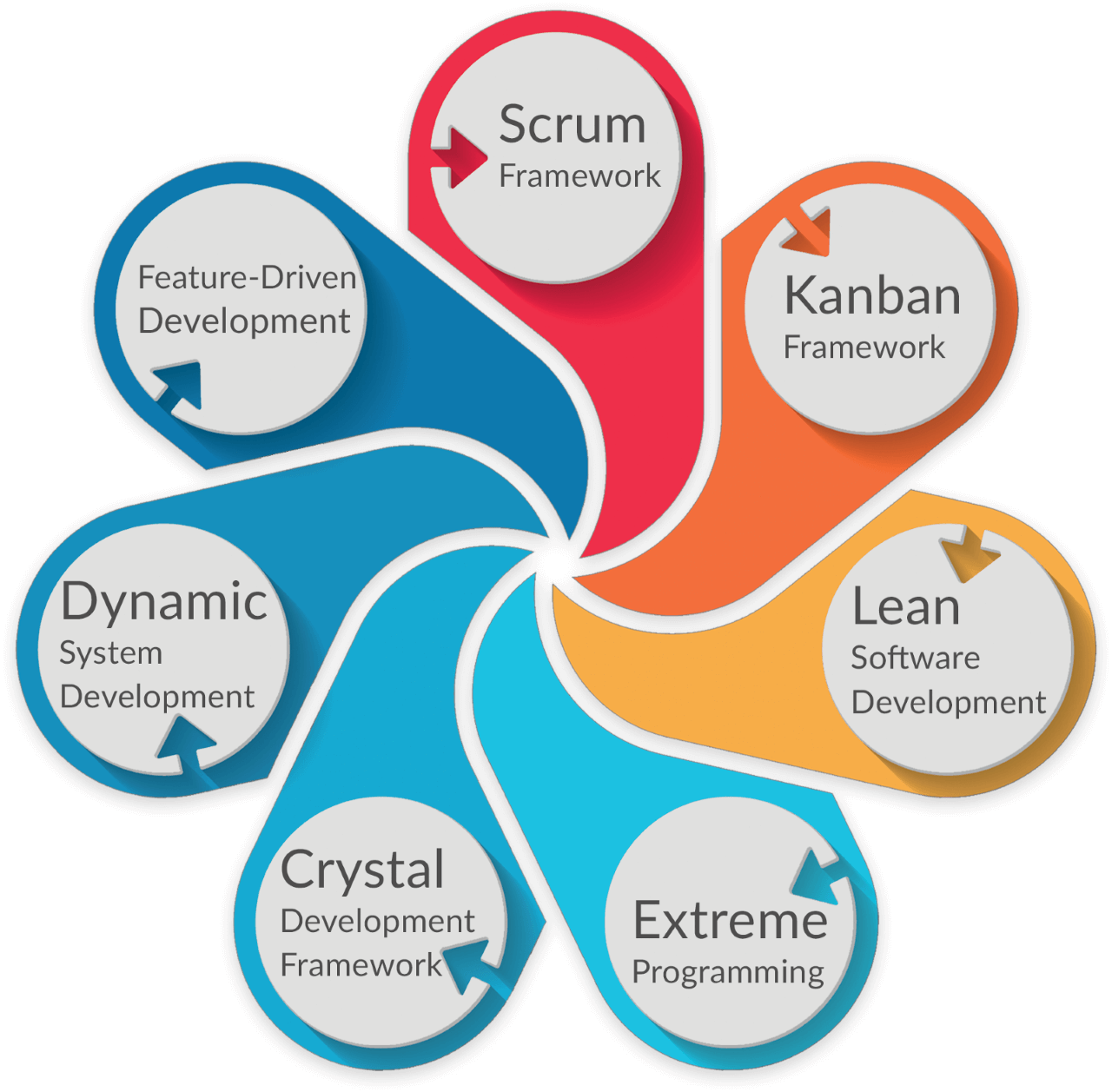
Agile framework
Agile frameworks join consistent planning, testing, coordination, and different types of development events. Agile systems are lightweight contrasted with traditional advancement techniques, which implies that guidelines and practices are kept to a base.
Scrum
This framework divides big projects into small tasks, making them easy to complete in shorter development cycles.
Crystal
The framework that makes the short-term projects involve teamwork in the same workspace is the Crystal framework.
Kanban
The framework deals with transparency in projects with visual and incremental so that the tasks are set so that they remain on board and categorized during the process.
Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM)
Dynamic Systems Development Method follows a process for governance foundation as it is a product delivery method and project management used by large organizations.
Feature-Driven Development
Feature-driven development requires strict documentation in the organization, and unlike other frameworks, it is laser-focused on the development team.
Which Agile Framework is Best?
You might have now come down to this point that there is no “best framework.” That is just best for your project group and your project work.
The news is that you don’t need to choose only one framework. You can join a few to accomplish the best potential outcomes for your project.
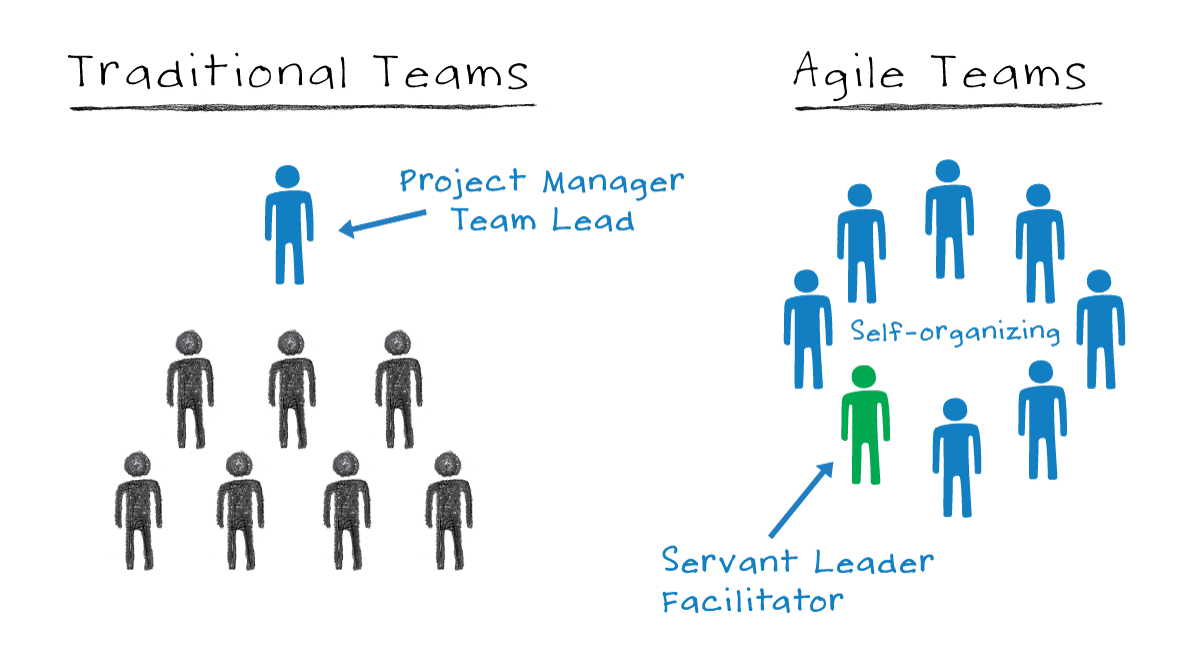
Traditional vs. Agile Project Management
In Agile management, unlike in the traditional project management stages, there is one critical contrast inside the “Adjust” stage, which characterizes Agile project management’s iterative nature. After you have made the vision for the item and arranged an emphasis plan, you continue to the “Investigate” stage. There, the point is to consistently deliver little expectations to the market instead of trusting that every one of them will be finished.
Then, at that point, in the “Adjust” stage, groups take part in short project audits with the clients who give their particular criticism. The thought is to adjust your future activities given that criticism and, if important, apply little alterations to what in particular has been conveyed.
Canadian Software Agency is the home to a remarkable specialized ability to function as a family. Their agile procedure-driven cooperative information is apparent in their smooth correspondence and force, which brings about the many projects they have conveyed.