In today’s digital world, users expect apps to be fast, reliable, and always available. Any downtime or delay can lead to frustrated users, lost revenue, and a damaged reputation. This is where high availability cloud solutions come into play. By designing apps that remain operational even during failures, businesses can ensure a seamless experience for their customers. Whether it’s an e-commerce platform handling thousands of transactions per minute or a SaaS product serving global users, high availability is no longer optional—it’s a necessity.
Building high availability applications might sound complex, but with cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, developers have powerful tools to achieve it. These platforms offer scalable infrastructure, automatic failover, load balancing, and disaster recovery options, making it easier to maintain uptime even during unexpected events. In this blog, we’ll walk you through practical steps to design and deploy high availability cloud apps, explain the benefits, and provide real-life examples. For instance, we recently implemented a solution for a project that involved handling sensitive operational data efficiently. You can check the case study here for more details.
By the end of this guide, you’ll understand how to leverage cloud services to build apps that are resilient, scalable, and reliable, keeping your users happy and your business running smoothly.
Understanding High Availability in the Cloud
High availability means ensuring that your application is always accessible, even if some components fail. It’s not just about uptime—it’s about creating a system that can handle unexpected failures without affecting users.
Cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer several tools to achieve this:
- Redundant Servers: Running multiple instances of your app so if one fails, others take over.
- Load Balancing: Distributing traffic across multiple servers to prevent overload.
- Automatic Failover: Switching to a backup system when the main one goes down.
- Geographic Distribution: Hosting servers in multiple regions to avoid local outages.
The key idea is to design apps so that failure in one area doesn’t take down the whole system. This approach ensures smooth operations, better customer experience, and a competitive edge.
Designing Your App for High Availability
Creating a highly available app starts with design. Here are the main steps:
1. Choose the Right Architecture
Use a microservices approach instead of a single monolithic app. Microservices allow independent scaling and easier recovery from failures. Each service can run in multiple instances across different regions.
2. Use Redundant Components
Ensure critical components like databases, APIs, and storage have backups. Most cloud providers offer managed database services with automatic replication across zones. For example:
- AWS RDS Multi-AZ
- Azure SQL Database with geo-replication
- Google Cloud Spanner
3. Implement Load Balancing
Load balancers distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers, preventing a single server from being overwhelmed. Examples include AWS Elastic Load Balancer, Azure Load Balancer, and Google Cloud Load Balancing.
4. Enable Auto Scaling
Auto-scaling allows your app to adjust capacity automatically based on demand. During peak hours, new instances are created; during low traffic, unused instances are shut down. This ensures optimal performance and cost efficiency.
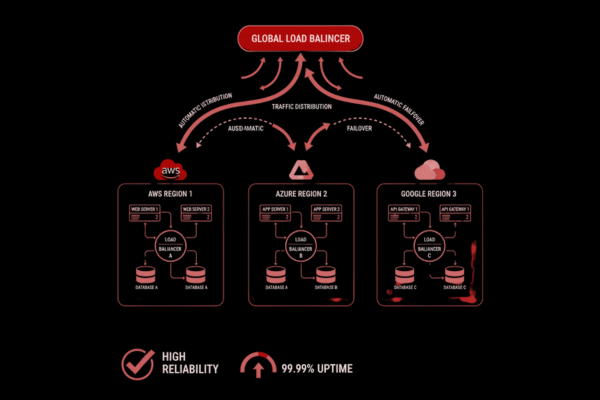
Deploying on AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud
Each cloud platform provides tools to support high availability cloud deployments.
AWS
- Availability Zones & Regions: Spread your resources across multiple zones for redundancy.
- Elastic Load Balancer (ELB): Distribute traffic automatically.
- Auto Scaling Groups: Adjust the number of instances based on demand.
- RDS Multi-AZ & S3: Reliable database and storage services with automatic failover.
Azure
- Availability Sets & Zones: Protect VMs from downtime during maintenance or failures.
- Azure Load Balancer: Ensures traffic is balanced and routed efficiently.
- Azure SQL with Geo-Replication: Provides database redundancy.
- Azure Traffic Manager: Route users to the nearest healthy endpoint.
Google Cloud
- Regions & Zones: Distribute workloads across multiple areas.
- Cloud Load Balancing: Global distribution for low latency and high availability.
- Cloud SQL with High Availability: Automatic failover for managed databases.
- Compute Engine Auto Scaling: Ensures your app can handle sudden traffic spikes.
Using these tools effectively allows you to build resilient applications that stay online even during unexpected failures.
Monitoring and Maintenance
High availability is not just about setup—it’s also about monitoring and maintenance.
1. Continuous Monitoring
Use cloud-native monitoring tools like AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, or Google Cloud Operations Suite to track system health, detect issues, and get alerts in real-time.
2. Regular Updates
Keep software, libraries, and dependencies updated. Security patches and bug fixes reduce the risk of downtime.
3. Disaster Recovery Planning
Have a disaster recovery plan that outlines steps to restore your system during failures. Backup data regularly and test recovery procedures.
4. Load Testing
Simulate traffic spikes to check how your app handles high load. This helps identify bottlenecks before they affect real users.
Benefits of High Availability Cloud Apps
Investing in high availability cloud architecture comes with multiple advantages:
- Improved User Experience: Users stay satisfied when apps remain responsive and reliable.
- Revenue Protection: Minimized downtime ensures continuous business operations.
- Scalability: Easily handle increasing user traffic without affecting performance.
- Cost Efficiency: Auto-scaling and optimized resource usage reduce unnecessary costs.
- Disaster Preparedness: Systems remain operational during failures or attacks.
Conclusion
Building highly available cloud applications might seem challenging at first, but with proper planning, the right architecture, and cloud-native tools, it becomes manageable. By leveraging AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, businesses can ensure their apps remain operational, scalable, and resilient under various conditions. High availability is not just a technical requirement; it is a strategic advantage that directly impacts user satisfaction, trust, and revenue.
Key steps to achieve high availability include designing for redundancy, using load balancers, enabling auto-scaling, and distributing resources geographically. Monitoring, maintenance, and disaster recovery planning are equally important to ensure long-term stability. These practices prevent service interruptions, allowing your team to focus on innovation rather than firefighting downtime issues.
In practical terms, applying these strategies can dramatically improve the performance and reliability of any application. For example, in a recent project where we handled sensitive operational data, implementing multi-region deployment and automated failover ensured that users could access services without interruption, even during peak usage or unexpected failures. You can explore the case study here to see a real-life implementation of these principles.
In conclusion, high availability cloud apps are essential for businesses that want to provide seamless user experiences, secure critical data, and maintain operational continuity. Investing in a well-architected, cloud-based system is an investment in the reliability and success of your digital products. By following these best practices, development teams can build apps that not only meet current demands but are also future-ready for growth and scalability. Achieving high availability may require effort, but the payoff in trust, performance, and user satisfaction makes it worthwhile.
FAQs
Q: What is a high availability cloud app?
A: An app designed to stay online and functional even during failures or high traffic.
Q: Which cloud is best for high availability?
A: AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud all provide robust tools for high availability.
Q: How do load balancers help?
A: They distribute traffic across multiple servers, preventing overload and downtime.
Q: What is auto-scaling?
A: Automatically adjusting resources to handle traffic changes efficiently.